Updated on:
Thu Jun 8 23:56:28 CEST 2017
Shortcuts
|
|
Current issues
- Test 2 blank: test2_17l.pdf and with solutions: test2_17l_solved.pdf.
Results have been posted in the "studia" server.
Students who passed the shortpath threshold: your grades will improve when Lab 6 is added. If you are still not satisfied then, take exam at no risk of loss (do not retake tests!). Anyway, congratulations!
If you think about Test1/Test2 retake, this will be available at the end of semester (on the day of Exam1, just after the exam). Please inform me in advance which test you want to retake.
- Office hours: Mon 16:30-17:00, room 454
- Lecture start: 23 Feb (Thu), 08:15-10:00, room 121
- Lab started with an introductory meeting on 6th Mar (Mon) 9:15, room CS202,
Regular labs will be on odd ("N_blue"group) or even ("P_green" group) Mondays, 8:15-12:00
- Lab groups have been assigned - please check them here
For "N_blue" group: Lab 1 is on 13th of March, 8:15
For "P_green" group: Lab 1 is on 20th of March, 8:15
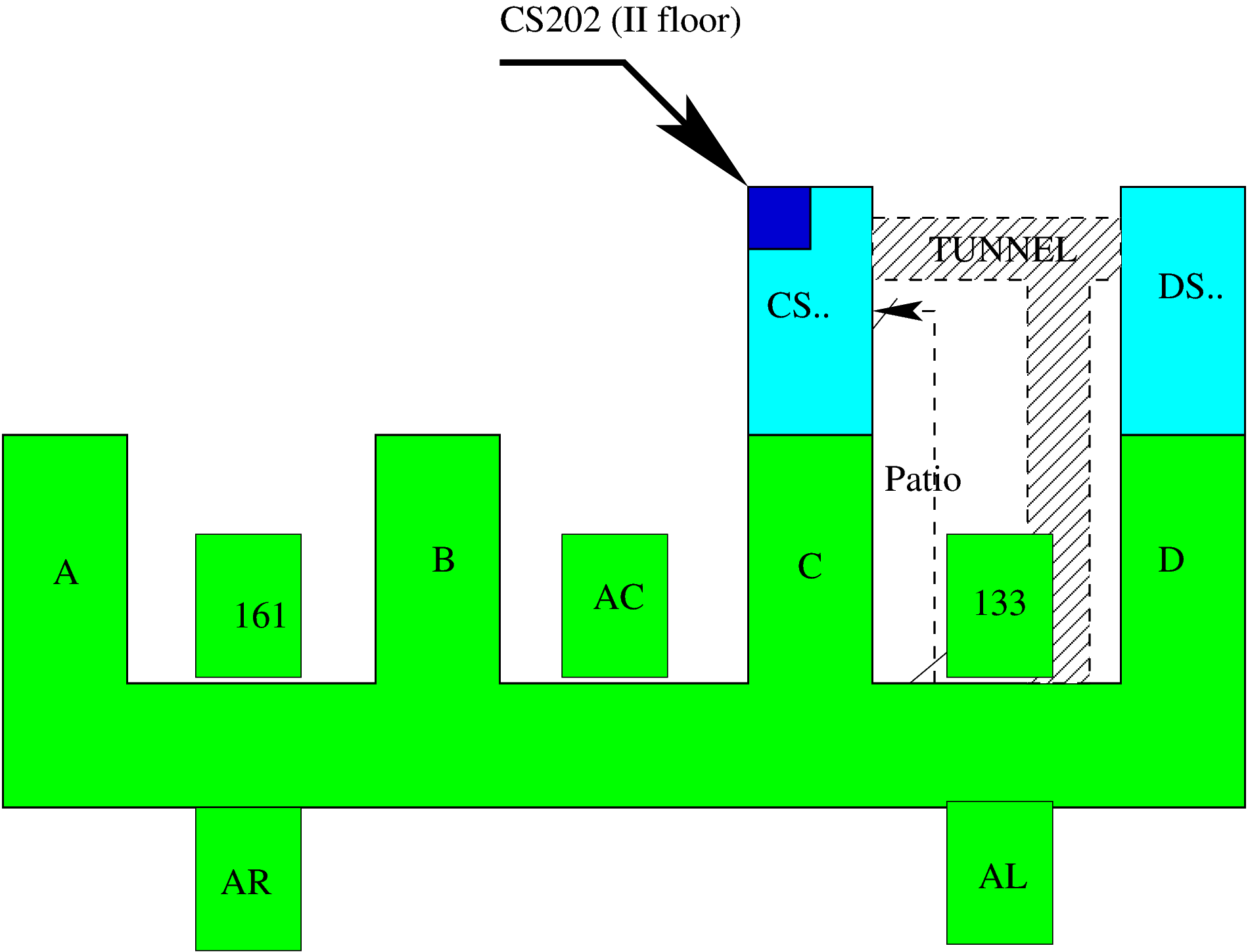
Where is Lab CS202?
|
What to do after EDISP?
If you are interested, choose elective courses:
- ETASP - (En) Techniques for Advanced Signal Processing
- EASP - (En) Adaptive Signal Processing
or in Polish:
TRA - Techniki Realizacji Algorytmów CPS
PSYL - Przetwarzanie SYgnałów w Labview
SRMP - Sygnały Radiolokacyjne i Metody ich Przetwarzania
CCM - Czasowo-Częstotliwościowe Metody przetwarzania sygnałów
APSG - Adaptacyjne Przetwarzanie SyGnałów
|
Home page of EDISP
(English) DIgital
Signal Processing course
semester 2017l (autumn/winter of 2016/17 acad. year)
Schedule
The lectures are on Thursday, room 121
08:15-10:00.
There are
lab exercises, 4 hours every second week, room CS202 (new wing C).
Labs will be on Mondays, 8-12 (N and P weeks) or Fridays 10-14 (P weeks; Fri is only available if the group is LARGE) , in
subgroups of not more than 12 students.
For the
introductory lab (lab0) we ALL met on
Mon, 6th Mar , 9:15 in room CS202.
Next lab (lab1) will
be
- Mar 13th (8:15-12) for N (Non-parity = parity odd) subgroup,
- Mar 20th (8:15-12) for P (Parity even) subgroup
"N" subgroup will have labs on Mondays marked
as "N" in the official
elka calendar (and "P" or "A" subgroup - on "P" Mondays).
Note that
- In some weeks the weekdays are swapped to equalize the semester,
- In some semesters the notion of "odd" (N) and "even" (P) in that calendar may be not as straightforward as taught within a basic algebra course.
A printable schedule is here
Books
Book base
The course is based on selected chapters of the book:
A. V. Oppenheim, R. W. Schafer, Discrete-Time Signal Processing,
Prentice-Hall 1989 (or II ed, 1999; also acceptable previous editions
entitled Digital Signal Processing).
Other books
- Steven W. Smith, The Scientist and Engineer's Guide to Digital Signal Processing - it is a free textbook covering some of the subjects, to be found here: http://www.dspguide.com/pdfbook.htm
The book is slightly superficial, but it can be valuable - at least as a quick reference.
- Edmund Lai, Practical Digital Signal
Processing for Engineers and Technicians, Newnes (Elsevier), 2003
seems also a simple but thoroughly written book.
- Vinay K. Ingle, John G. Proakis, Digital Signal Processing using MATLAB, Thomson 2007, Bookware Companion series
Supplementary books I found in our faculty library:


Additional books available in Poland:
- R.G. Lyons, Wprowadzenie do cyfrowego przetwarzania sygnałów
(WKiŁ 1999)
- Craig Marven, Gilian Ewers, Zarys cyfrowego przetwarzania sygnałów,
WKiŁ 1999 (simple, slightly too easy)
[en: A simple approach to digital signal processing, Wiley & Sons, 1996]
- Tomasz P. Zieliński, Od teorii do cyfrowego przetwarzania sygnałów,
WKiŁ 2002 (and next edition with slightly modified title)
Please remember:
- there are notation differences between lecture and "dspguide"
- The official book is Oppenheim & Schafer (though notation is
sometimes different too)
- no book is obligatory as it is hard to get O&S, and
other books do not cover the subject fully.
Probably the best choice is to buy a used copy of O&S.
It'll serve you for years, if you are interested in DSP. And it contains a lot of PROBLEMS to solve and learn!
Ingle/Proakis is also a good book (and you may be able to buy a new or almost new copy).
If you know LANG=PL_pl - you may prefer to buy/borrow a laboratory scriptbook for CYPS, which is in
Polish language (Cyfrowe Przetwarzanie Sygnałów, red. A Wojtkiewicz,
Wydawnictwa PW).
Supplementary material
In the course of the semester you may realize that your math knowledge is pulling you back. This is normal. DSP is a practical math usage, so you need maths. Go back to your math books and notes, and look for knowledge in the web.
Wikipedia may be too formal, but try it. Then, there is a number of course notes. I appreciated very much Paul DAwson's page when I looked for a simple example of a h(n) which convereges to zero, yet doesn't provide stability.
Course aims
In other words -- what I expect you to learn, or what I will check when it comes to grading.
A student who successfully completes the course will:
- know the mathematical fundamentals of discrete-time (DT) signal processing: DT signals, normalized frequency notion, DT systems, LTI assumption, impulse response, stability of a system
- understand the DT Fourier transforms and know how to apply them to simple DT signal analysis
- know basic window types and their usage for FT and STFT
- understand the description of a DT system with a graph, difference equation, transfer function, impulse response, frequency response
- be able to apply Z-transform in analysis of a simple DT system
- understand filtering operation and the process of DT filter design; be able to use computer tools for this task
- know the basic attributes of a Digital Signal Processor (differences w.r.t. general purpose processor, ways of speeding up the calculations, fundamentals of block diagram and programming)
- understand 2D signal processing basics: 2D convolution/filtering, 2D Fourier analysis
- be able to use a numerical computer tool (Matlab, Octave or similar) for simulating, analyzing and processing of DT signals
Lecture slides
(You may always expect hand-made corrections and inserts at the
lecture....)
- Lecture 1 slides: (intro, signals)
newerlect1.pdf
- Lecture 2 slides: (sampling, frequency)
newerlect1.pdf (from slide 12)
and
newerlect2.pdf
- Lecture 3 slides (frequency, FT od periodic signals, DFT):
(idea of a transform, FT - Fourier Transform of L2 signals) newerlect2.pdf
- Lecture 4 slides - DFT: newerlect2.pdf (continued)
and windowing \& FFT newerlect3.pdf
- Lecture 5:
FFT - newerlect3.pdf
Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT, instantaneous spectrum): newlect6.pdf
- Lecture 6
FFT - Fast Fourier Transform
STFT - Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT, instantaneous spectrum): newlect6.pdf
LTI systems, convolution, z-transform
lect_lti_z.pdf
- Lecture 7 z-transform
lect_lti_z.pdf continued
HOMEWORK1 will be given (due 20.04)
- 13 Apr - holidays start...
- Lecture 8 (20 Apr 2017) filters, filter design:
lect_filt.pdf
Filters - advanced design, tips, tricks lect_filtadv.pdf
HOMEWORK1 (due in the middle break)
- Lecture 9 (27 Apr 2017): Test I
- One hour test I, 10pts worth: bring YOUR OWN notes (handwritten on paper or on printed
lecture slides). No books, no photocopies of other person
notes.
The test will cover the subjects which were in the Homework1 i.e. up to (and including) LTI systems and comvolution/impulse response.
Example test:test1_078a.pdf
More examples w/solution: down in the page
-
Filters lecture - continued.
- 4 May 2017: NO LECTURE
- Lecture 10 (11 May 2017):
Filters lecture - continued.
- Lecture 11 (18 May 2017):
Implementing DSP lect_implem.pdf
Homework2 start - please download from homew2_2008plus.pdf.
- Lecture 12 (25 May 2017):
2D signals: newlect13_2d.pdf
and
signal processing
for data compression
Homework 2 due today
- Lecture 14 (1 Jun 2017):
2D signals continued
signal processing
for data compression
Advanced techniques;
- Lecture 13 (8 Jun 2017):
test II
example test here; in problem 1a use M=6 or 4 (not 5, as it has to be even)
More test examples in test examples section.
- THE END OF SEMESTER
Old slides below - this marker will be moved with slide update
- Lecture 11 (22 Dec 2016):
More on implementation tricks
and 2D signals:
newlect13_2d.pdf
Homework2 start - please download from homew2_2008plus.pdf.
- Lecture 12 (05 Jan 2017):
2D signals continued: newlect13_2d.pdf
and
signal processing
for data compression
Homework 2 due today
- Lecture 13 (12 Jan 2017):
test II
example test here; in problem 1a use M=6 or 4 (not 5, as it has to be even)
More test examples in test examples section.
- Lecture 14 (19 Jan 2017):
Random DT signals;
- Lecture 15 (26 Jan 2017):
Advanced techniques;
- THE END OF SEMESTER

- When: Thu 23.06, 11-14 (preliminary session schedule), where: 120 Exam 1
pen, pencil, calculator and your own notes
plus lecture slides.
Copies of solutions for homeworks/tests/exams
are NOT allowed.
The exam covers ALL the course matter. There are "Problems" (longer)
and "Questions" (shorter), for total of 90 minutes.
If you fail Ex1 you are still entitled to take Ex2.
Students who earned the "shortpath" grade may take the ex1 or ex2
without any risk - better grade counts
Just after Exam1 there will be a possibility to re-take test1 and/or test2.
Please mail me to declare if you want it.
A re-taken T1/T2 does NOT count towards shortpath
- When: Wed 29.06 11-14 (preliminary session schedule), where: 120 Exam 2
Examples of tests
Use them for study. Learn methods, not solutions.
Exam tests 2007
One test. Another test.
There is no guarantee that the current test be identical ;-). It
will be similar (the lecture was similar), but I might also put
more focus on different subjects. The only base is the lecture content
(live one, not only the published slides ....).
The main rule: exam covers the whole course content (sampled),
including the T1(H1)+T2(H2) area and also the lectures after the
H2.
Exam tests 2009 w/solution discussion
Exam version A
Exam version B
- In both cases the signal was sampled correctly
(fs>2f)
- To calculate N0 it was enough to count no. of
samples in period (or divide fs over f). Answer was
10(A) or 6(B). For N0 samples in period,
θ0 was equal to 2π/N0.
- K-size DFT will have K discrete samples over <-π, +π)
(we include -π, and exclude +π , but
due to periodicity of spectrum it is only a
convention)
for a cosine, only two samples are non-zero: at k such that
θk=±θsignal. Form the
definition of θk you will see that this is
for k=±4 (this is the result of taking K=4N0).
- You may label frequency axis with
k=-K/2,....-1,0,1,...K/2 or with its periodic equivalent
K-K/2,....K-1,0,1,...K/2
to label with θ just use
the expression for θk.
-
- H(z)=Y(z)/X(z) is easily obtainable from the time equation. It
was
-0.2(1+z-1)/(1-0.8z-1) [A]
0.2(1-z-1)/(1+0.8z-1) [B]
- Zeros are roots of numerator: -1 [A] or +1 [B]
Poles are roots of denominator: +0.8 [A] or -0.8 [B]. They are
inside unit circle, so the system is stable (but I didn't
ask...)
- Example graph:
 - please
find a_0, b_0, b_1 by yourselves. If you are smart, you may save
one multiplication by 0.2 (this is left as exercise to you).
- please
find a_0, b_0, b_1 by yourselves. If you are smart, you may save
one multiplication by 0.2 (this is left as exercise to you).
- For x(n)= shifted delta, (a limited energy signal)
you may take the impulse response
and shift it appropriately. To find h(n) it is easiest to split
H(z) into two fractions: (shown for [A], for [B] change some signs)
0.2(1/(1-0.8z-1)+z-1/(1-0.8z-1))
and lookup the inv.Z of 1/(1-0.8z-1) in the
table. The final result is a sum of two identical exponentials
shifted by 1 in time. Then, you shift h(n) to proper position....
- For x(n) = 1-(-1)n (a periodic signal) we see a DC
component and a periodic component exp(jπn) with frequency of
π. We find numerical values of
H(0)=(2 or 0) and H(π)= (0 or -2) by substituting exp(0) and exp(π) for z, and
finally
y(n)=H(0)-H(π)·(-1)n
- The response was symmetrical around its midpoint (n= 2 or
4). Thus, it was a repsonse of a zero-phase filter delayed by 2 or
4.
- phase is linear φ=-(2 or 4)θ
delay is constant and equal to (2 or 4)
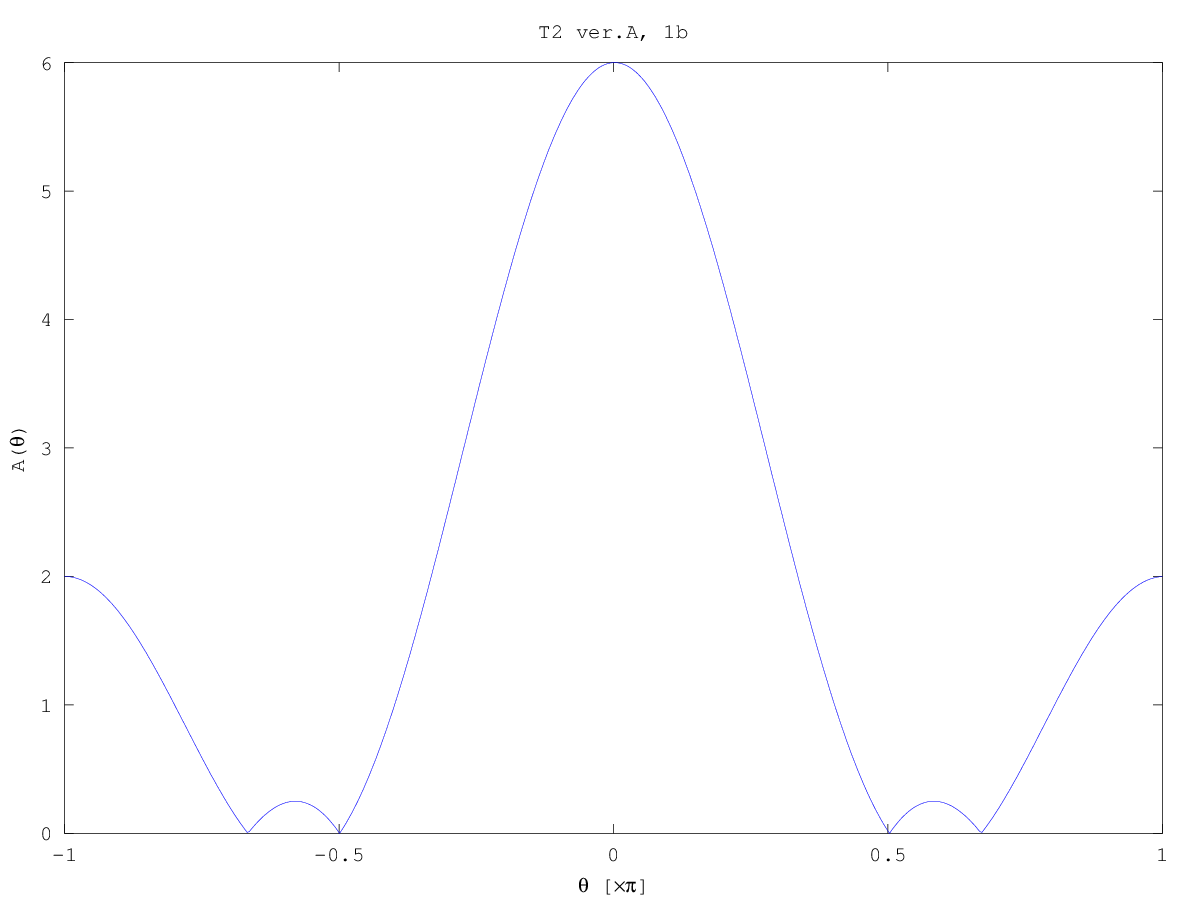
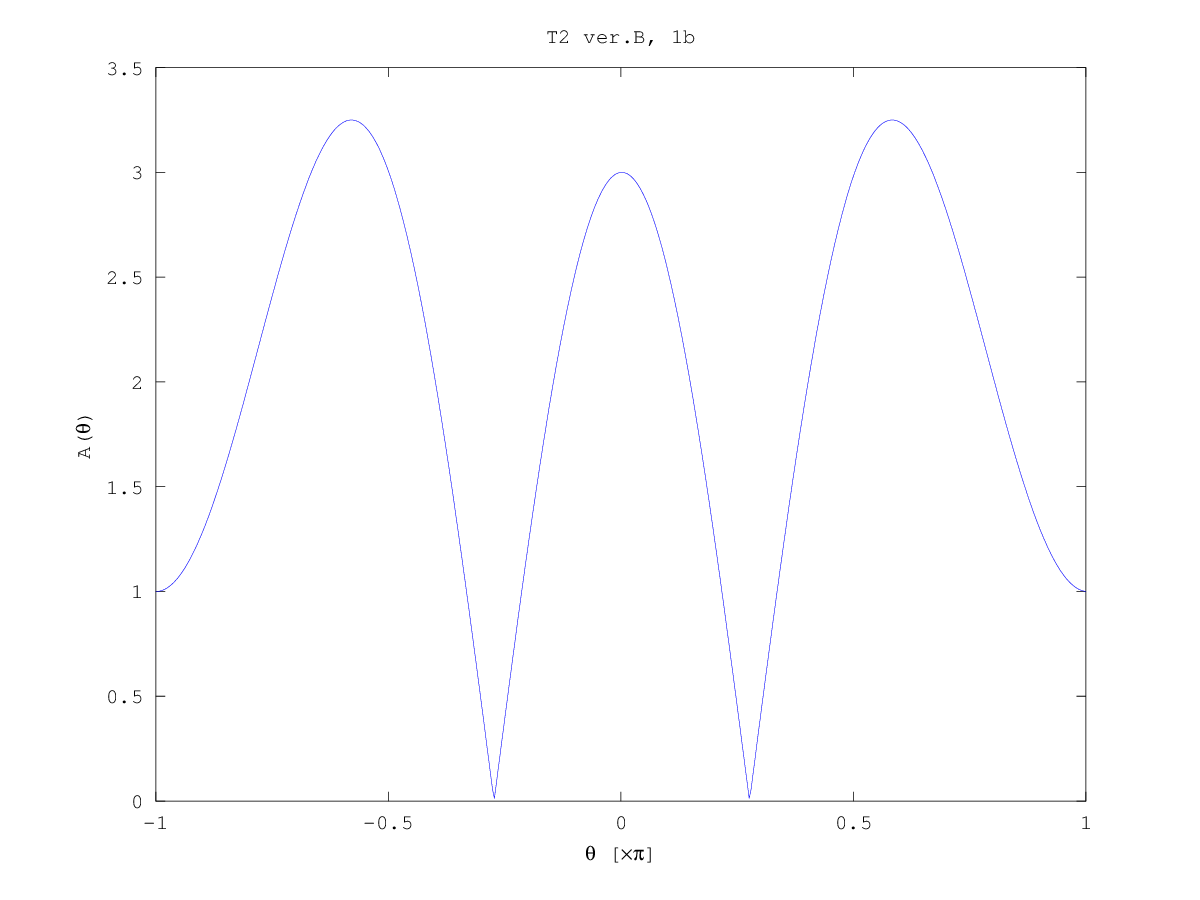
- The response of filter is a rectangle modulated by
exp(jπn). Thus, the characteristics is a
sin(θL/2)/sin(θ), shifted to π. You may find the
mainlobe width, you may plot exactly zeros of A(θ) etc.
- Time resolution is proportional to time duration of window,
frequency resolution - to mainlobe width (which is prop. to 1/K
....).
Rectangular window has narrowest mainlobe possible, but high
sidelobes; so it is good for resolving signals close in frequency,
but without large difference in amplitudes.
Any other window will have wider mainlobe (so poorer resolution in
f).
-
There was nonlinearity introcuced by product of two samples (linear is
multiplication by a constant only).
Saying "stable=yes because of BIBO" was not enough; "because FIR" was
enough; if you call BIBO, you have to prove it by finding relation
between bound of input Bx and output By.
- LP filter with passband of π/4 (see the "lecture 17").
- Many shorter is better: by averaging we reduce the variance
of estimate. (variance is huuuuuge with single FFT)
- β (some call it α) controls the shape of window -
effectively the sidelobes level (high β - low sidelobes). Is
high β better? yes, if you are concerned with sidelobe level;
but remember that you pay with wider mainlobe (There Ain't No
Such Thing As A Free Lunch)
- Inv FT is calculated by summation when the spectrum is
discrete ([B], periodic signal) and by integration when the
spectrum is continuous ([A], limited energy signal).
- 3 buses are for opcode, data1 (signal), data2
(coefficient).
Any instruction with dual move uses all three,
e.g MAC instruction needs 2 data, so it is nice that we can load
data in the same cycle
in 56002 it can be coded as:
mac a,b x:(r0+),x0 y:(r4+),y0
- Trivial
- def: order of n^2, FFT: order of n log2(n)
- y(n) length is, maximally, (length of h(n))+(length of
x(n))-1. K=M+N-1. Here, we were asked to find M knowing K and
N. Answer is, as you may guess, M=K-(N-1)
- The clue is in word "maximally". It may happen that for
certain signal (e.g in the stopband....) the y(n) is shorter.....
Exam test 2012/13
Exam sheet
T1/T2 test examples
Please note that the solutions are NOT a model ones to copy and paste. In some cases a "full score" student solution to the test needs a bit of explanations, and in many cases my solution is too large - I wanted to show different possibilities or broaden an example.
To summarize - don't learn by heart. Learn by brain. Try to solve the missing versions of tests.
Test1 2010/11 ver.A problems
Test1 2010/11 ver.B problems
Test1 ver.B solutions
Test1 ver.A solutions
Test2 2016L ver A. solved
Test2 2016L ver B. (do it yourself)
Test2 (ver.A) and solutions
Test2 (ver.B) (do it yourself!)
Also, think first, act later.
- If you see a system - what type of system it is? LTI? What consequences arise from this?
- If you see a signal - is it limited energy? periodic?
- Which tool to use for LE? Which one for periodic? Which FT definition is appropriate?
- Is the plot you see in time or in frequency?
- Is the plot you have to sketch - in time or freq domain?
- Will the sketch requested be continuous or discrete? periodic? Will it have some symmetry? Is the function real-valued or complex? Maybe we are plotting abs()?
- maybe the function in freq can be expressed as "real times exp(j n0 theta)" because in time it is "symmetrical but shifted by n0"? How much is n0? (If in freq domain - shifted by θ0 - how much is this? )
- Signal is causal? Don't forget u(n) then.
- See -1? Try exp(j pi) instead. See exp(j pi)? Try (-1)....
When solving at home, you may use matlab or octave to do calculations like (1-j)/(1+j) (or to verify your calculations). You may also use these tools to show plots. Then try to understand why it is like you see - no Matlab at the exam, please :-).
Test1 2013/14 ver.A problems
- Max score was 13, I assume 10 is OK, and +3 is a bonus.
- Typical errors as I commented by email on your homework still show up.
- Hints:
- Impulse response is useful if system is LTI (Linear AND Time-Invariant -- you must verify both!)
Stability is verified by finding M such that By=M Bx; one way to find M is to calculate ∑ |h(n)|. Remember that h(n) → 0 is NOT enough (look here for an example)
- Remember that fn or N are UNITLESS (don't use units like Hertz or seconds) -- they are ratios of f/fs or just number of samples
Common error -- forgetting that there is N0 and N, and N must be an integer (N=19 [A] or 9 [B])
- FFT complexity calculation was simple (answer: [A] 48 ms, [B] 2 ms)
- DTFT was either 2cosθ or -2jsinθ. The task was to plot AMPLITUDE |X(θ)|, then to recall that DFT-8 will be just 8 samples of X(θ)
- Formula N+L-1 is good as a maximum length of convolution if we don't know exactly signals. In this case h(n) was a short rectangular pulse, x(n) -- two well-separated deltas, so in the output we got just two copies of h(n). ([A]:10, [B]:14, however I gave 1/2 score for correct application of L+N-1)
Put this code in Octave or Matlab:
x=zeros(1,100);
n=[1:100]-10;
x(n==0)=1;
x(n==40)=1;
figure(1);
stem(n,x); title('x(n)');axis([-20 100 0 1.2]);
h=ones(1,5);
figure(2);
stem(0:4,h); title('h(n)');axis([-20 100 0 1.2]);
figure(3)
y=conv(x,h);
stem([1:length(y)]-10,conv(x,h));axis([-20 100 0 1.2]);
- xs(n) was a SUM of x(n) with manipulated x(n):
1. shifted by N → X(k)⋅ exp(-j N θ_k) ; happily this factor is always =1;
2. inverted in time → X(-k) (or X*(k) for real signals)
Some students applied linearity idea in the argument of X(k) (WRONG!!!! Do it only on X, not on k)
Test 2 (2013/14) solutions sketch
Computer plots:
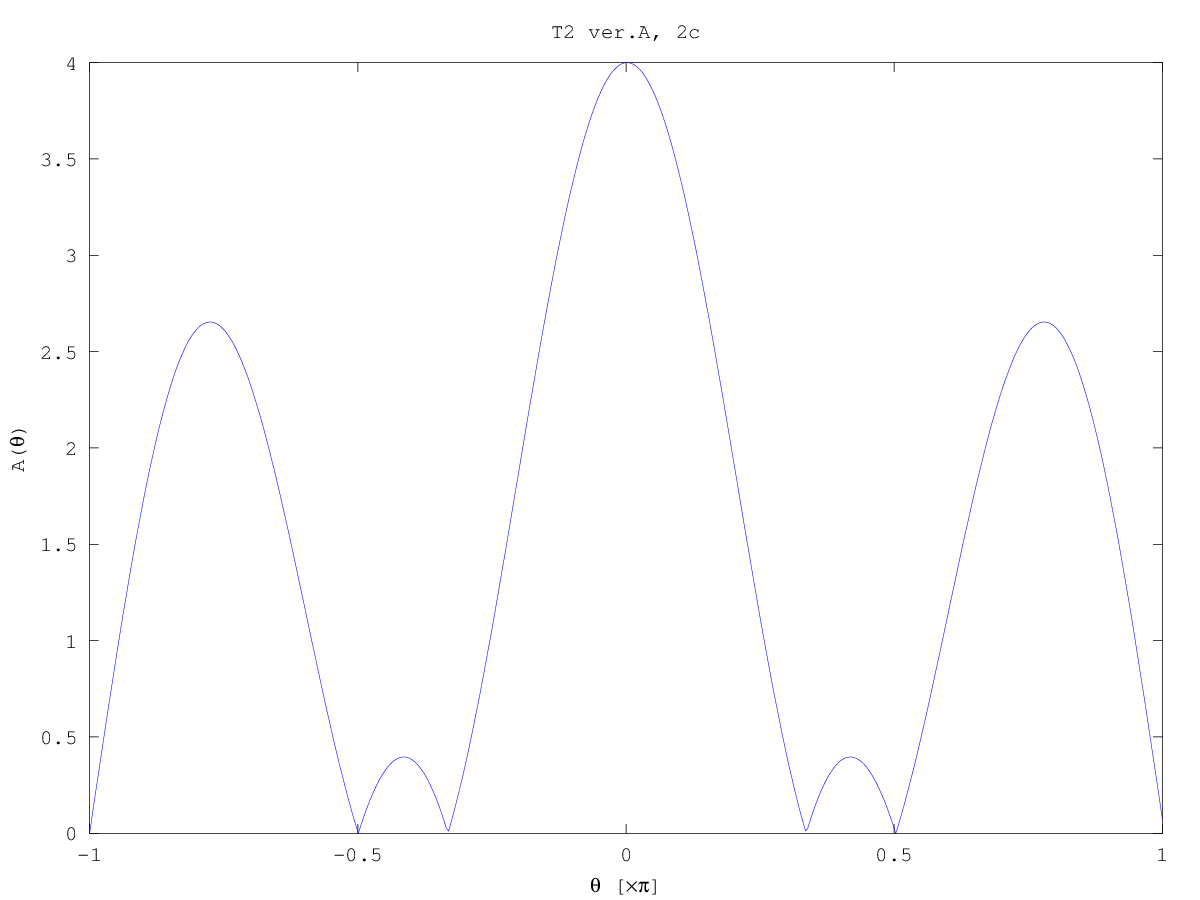
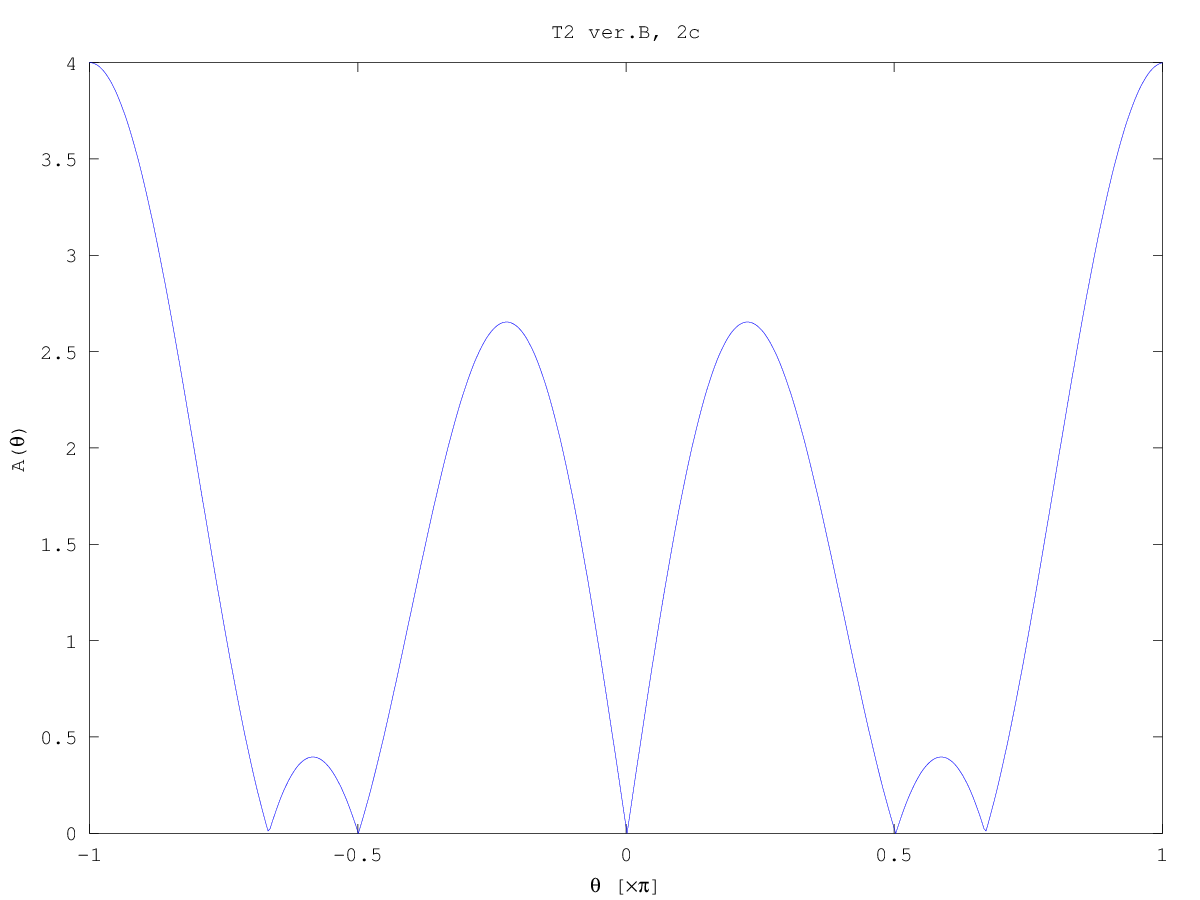
Test 1 (2016z) solved
Lab info: example lab exercises
The labs will be taught by
Lab rules (do's/dont's, grading)
Disclaimer:
These are called "examples" to underline the fact that they are not
official. Some of them need review....
Openly speaking, they are exercise sets current at the
time of posting. I reserve the right to make some important
modifications before the actual lab, to give different sets to
different groups etc. (and I usually DO review the text before giving
it....).
Lab exercises:
Students do not need to print these
scripts -- the official lab instructions will be available at the lab.
Old instructions below - this marker will be moved with updates
Past things archive (Attic)
dr inż. Jacek Misiurewicz
room 454 (GE)
Office hours: Mon 16:30-17:00 (or by e-mail appointment)
Institute of Electronic Systems

Instytut Systemów Elektronicznych
Institute of Electronic Systems
email:jmisiure@elka.pw.edu.pl
This page is "Continuously Expanding".///////////////////////










 - please
find a_0, b_0, b_1 by yourselves. If you are smart, you may save
one multiplication by 0.2 (this is left as exercise to you).
- please
find a_0, b_0, b_1 by yourselves. If you are smart, you may save
one multiplication by 0.2 (this is left as exercise to you).




